The U.S. government also borrows money from itself through a process called “intragovernmental debt.” Intragovernmental debt is the money that the government owes to its own agencies, such as Social Security and Medicare. In this blog post, you will come to know that Who Does the U.S. Borrow Money From. Here is Exceptional Reason.
Who Does the U.S. Borrow Money From?
The amount of money that the U.S. government borrows each year is called the “national debt.” The national debt is currently over $30 trillion.
There are a few reasons why the U.S. government borrows money. One reason is to finance its budget deficit. The budget deficit is the difference between the government’s spending and its revenue. When the government spends more money than it collects in taxes, it has to borrow money to make up the difference.
Another reason why the U.S. government borrows money is to invest in infrastructure and other long-term projects. The government may borrow money to build roads, bridges, and other public works projects. It may also borrow money to fund research and development.
The U.S. government also borrows money to respond to emergencies, such as natural disasters or wars. When the government needs to spend money quickly to respond to an emergency, it may borrow money to do so.
There are a few risks associated with the U.S. government’s debt. One risk is that the government may not be able to repay the debt. If the government defaults on its debt, it could damage its credit rating and make it more difficult to borrow money in the future.
Another risk is that the government’s debt could lead to inflation. When the government borrows too much money, it can cause the money supply to grow too quickly. This can lead to inflation, which is a general increase in prices.
The U.S. government manages its debt through a variety of policies. One policy is to issue bonds. Bonds are a type of loan that the government sells to investors. When investors buy bonds, they are lending money to the government.
Another policy that the government uses to manage its debt is to raise taxes. When the government raises taxes, it collects more money in revenue. This can help to reduce the budget deficit and the national debt.
The U.S. government also uses a policy called “deficit spending.” Deficit spending is when the government spends more money than it collects in taxes. This can help to stimulate the economy in the short term, but it can also lead to an increase in the national debt.
The U.S. government’s debt is a complex issue with a variety of implications. It is important to understand the different factors that contribute to the debt and the risks associated with it.
Details Information on it
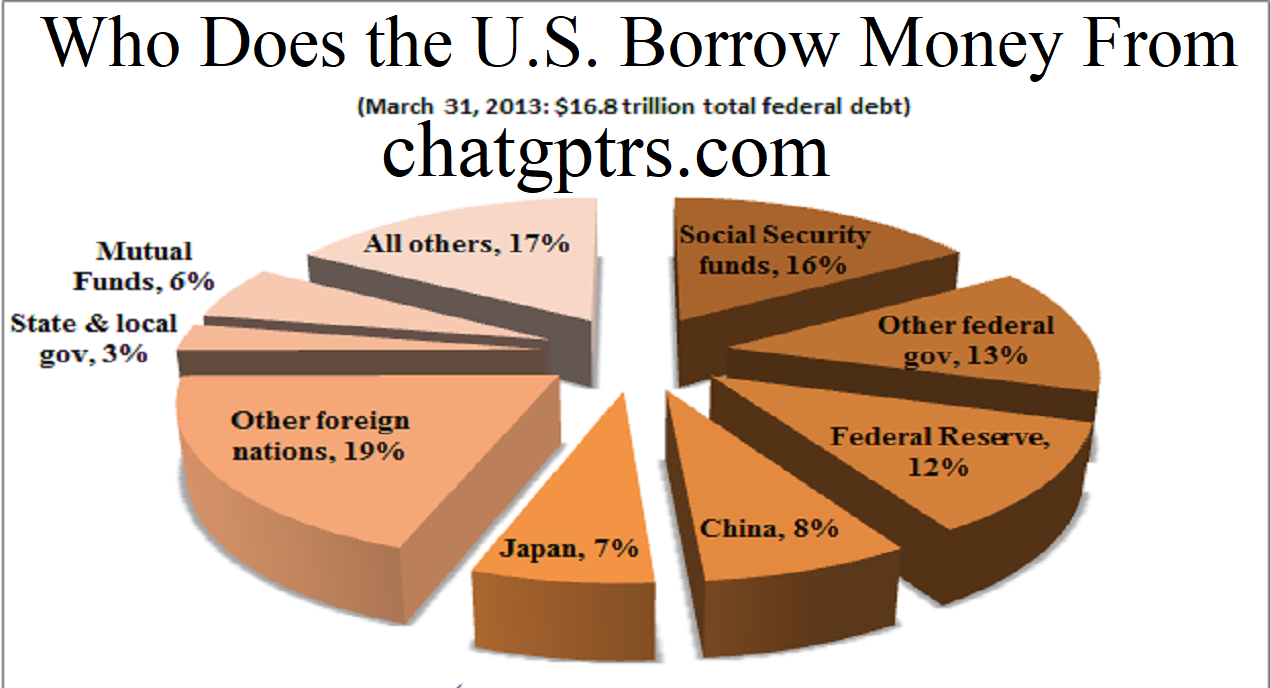
The Federal Reserve
- The Federal Reserve is the central bank of the United States. It buys and sells U.S. Treasury securities in order to influence the money supply and interest rates.
Foreign countries
- Foreign governments, central banks, and other institutions buy U.S. Treasury securities as a way to invest their money and earn a safe return.
Individual investors
- Individual investors buy U.S. Treasury securities as a way to save for retirement or other financial goals.
Mutual funds and other investment vehicles
- Mutual funds and other investment vehicles buy U.S. Treasury securities as a way to diversify their portfolios and reduce risk.
Intragovernmental debt
- The U.S. government also borrows money from itself through a process called “intragovernmental debt.” Intragovernmental debt is the money that the government owes to its own agencies, such as Social Security and Medicare.
Why the U.S. Government Borrows Money?
Here are some of the reasons why the U.S. government borrows money:
- To finance its budget deficit. The budget deficit is the difference between the government’s spending and its revenue. When the government spends more money than it collects in taxes, it has to borrow money to make up the difference.
- To invest in infrastructure and other long-term projects. The government may borrow money to build roads, bridges, and other public works projects. It may also borrow money to fund research and development.
- To respond to emergencies, such as natural disasters or wars. When the government needs to spend money quickly to respond to an emergency, it may borrow money to do so.
Risks Associated with the U.S. Government’s Debt:
Here are some risks associated with the U.S. government’s debt:
- The government may not be able to repay the debt. If the government defaults on its debt, it could damage its credit rating and make it more difficult to borrow money in the future.
- The government’s debt could lead to inflation. When the government borrows too much money, it can cause the money supply to grow too quickly. This can lead to inflation, which is a general increase in prices.
Some Policies:
Here are some policies that the U.S. government uses to manage its debt:
- Issue bonds. Bonds are a type of loan that the government sells to investors. When investors buy bonds, they are lending money to the government.
- Raise taxes. When the government raises taxes, it collects more money in revenue. This can help to reduce the budget deficit and the national debt.
- Deficit spending. Deficit spending is when the government spends more money than it collects in taxes. This can help to stimulate the economy in the short term, but it can also lead to an increase in the national debt.
FAQs about who the U.S. borrows money from:
What is the national debt?
The national debt is the total amount of money that the U.S. government owes to its creditors.
How much is the national debt?
The national debt is currently over $30 trillion.
Who owns the national debt?
The national debt is owned by a variety of investors, including the Federal Reserve, foreign governments, and individual investors.
How does the government pay off the national debt?
The government pays off the national debt by collecting taxes and by issuing new debt.
What are the risks of the national debt?
The national debt could lead to inflation, a decrease in the value of the dollar, and a loss of confidence in the government.